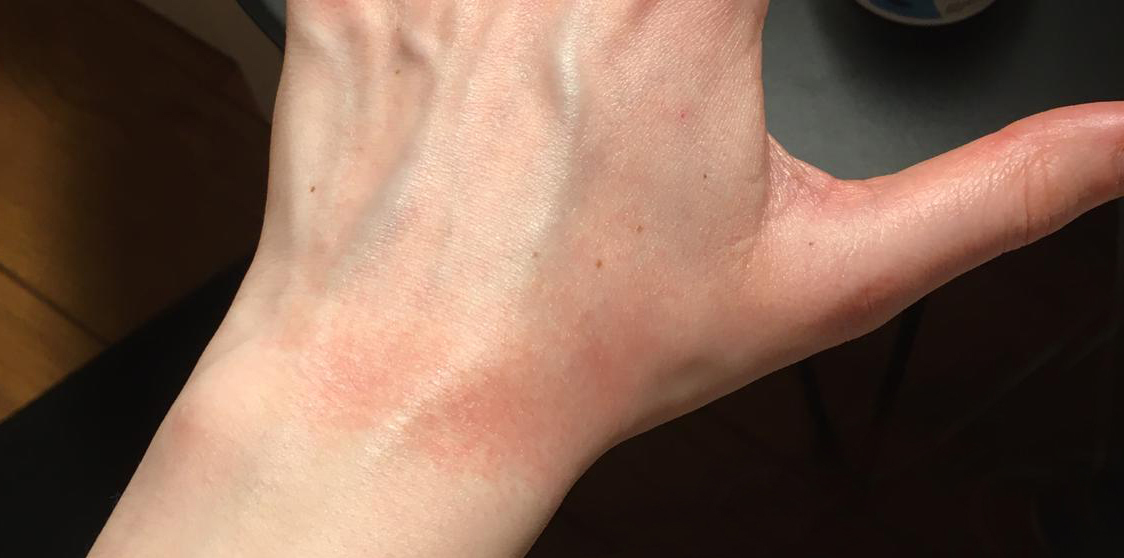
Due to frequent handwashing and disinfection during the pandemic, there is a risk of skin irritation, dryness, cracks, and the development of eczema. Eczema develops as a result of prolonged exposure to mild irritants such as water, detergents, and disinfectants. Healthy skin has a slightly acidic environment with a pH of 5.5, but the pH of soaps is alkaline and can reach up to 11. Acids with a pH below 2 are also harmful to the skin. Alkaline soap residues after washing can damage the skin's protective lipid layer. If this layer does not recover, skin inflammation may occur.
Handwashing
It is recommended to avoid using bar soap and instead opt for liquid soaps, as they are less alkaline. It is important to replace soaps with oil-based cleansers (shower oils, ideally with a pH of 5.5). Use fragrance-free cleansers and lukewarm water. Oil-based cleansers bind dirt and dead skin cells without damaging the lipid barrier. Rings should be removed before washing, as dirt and soap residues can accumulate under them.
Disinfection
For hand disinfection, gels should be preferred, as they do not damage the skin's lipid barrier as much as alcohol solutions. It is better to use disinfectant gels containing glycerol. It is important to let the gel dry completely.
Moisturizing
After every wash, it is essential to apply basic creams. Using basic creams is important as they prevent water loss from the skin and help maintain the skin's protective lipid layer. As we know, water and oil do not mix. For the basic cream to penetrate the skin, water and oil/wax/fatty acids must be galvanically bonded. Whether the product is an ointment, cream, or lotion depends on the ratio of water to fatty acids/waxes/oil in the formula.
Ointments contain the most oil/waxes and fatty acids. They may feel greasy, but they are the most effective at preventing skin dryness.
Lotions contain the least oils, making them less effective, while creams are in between in terms of effectiveness.
Ointments are recommended for dry skin without signs of inflammation, while creams and lotions are suitable for swollen and already inflamed skin.
In case of dry skin, basic creams can be applied to the hands overnight, with cotton gloves worn over them. There is no limit to the number of times basic creams can be used, but if the need for their use continues to increase over time, it may be a sign that medication is required.